App general settings
Only Jira admins have permission to manage Agile Test general settings.
To access App Settings
Select the wheel icon (⚙️) in the top-right corner to open Jira administration.
Select Apps (under section Jira admin settings)
Find Agile Test on the left panel.
Below are the configuration settings that can be managed for instances.
1. Health Check
The Health Check feature in AgileTest ensures that all necessary configurations are correctly set up in your Jira instance.
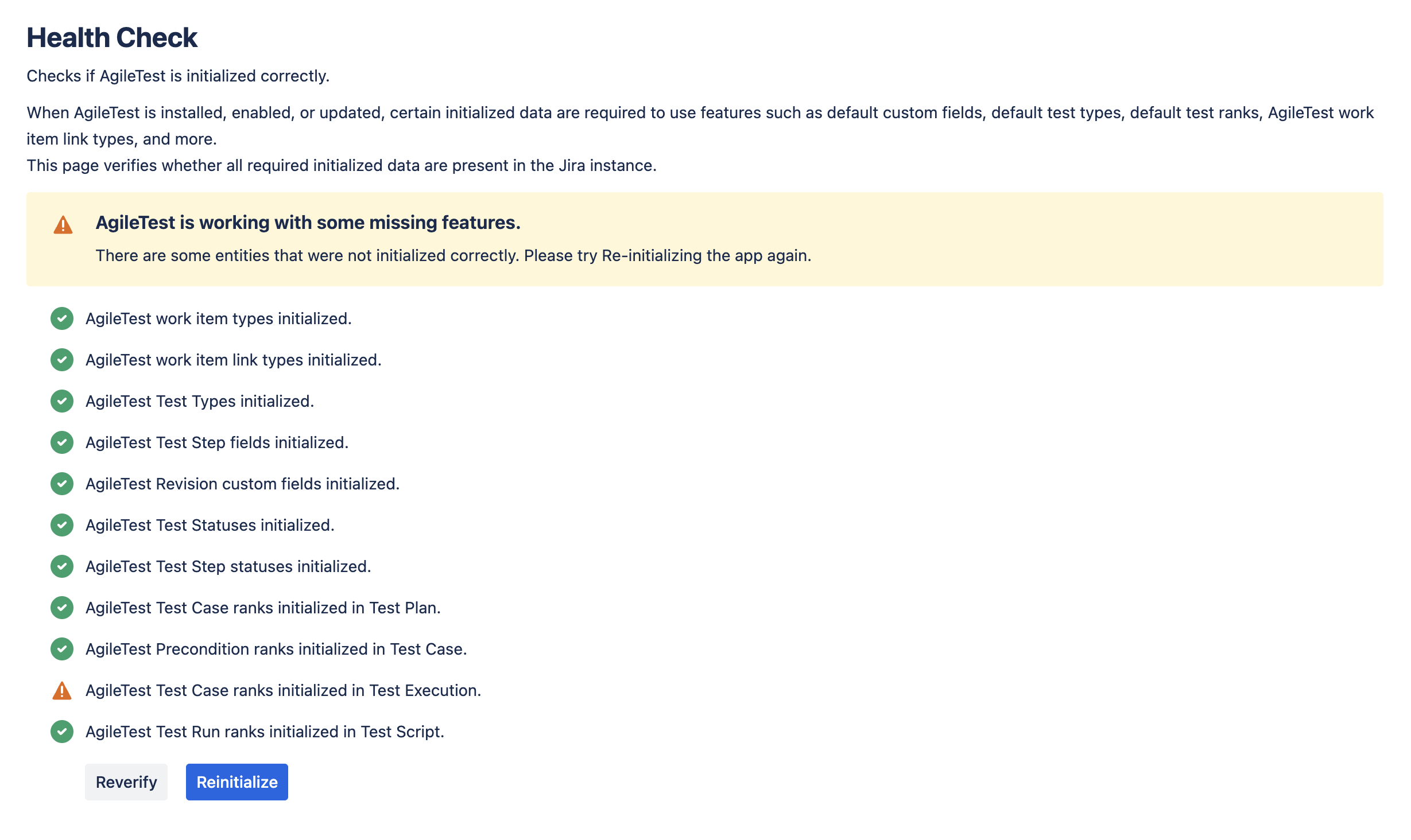
When AgileTest is installed or updated, it requires certain entities (like test types, custom fields, and ranks) to be initialized. The Health Check verifies that these entities are present and properly configured. Health Check monitors the following entities:
Work Item Types: Make sure test plans, test cases, and other work items are properly configured.
Test Types, Test Steps, Test Statuses: Verify that all test configurations are initialized and available for use.
Custom Fields & Revision Fields: Ensure that the necessary custom fields for test cases and revisions are initialized correctly.
Test Case Ranks and Test Execution: Check that test case ranks and execution statuses are set up correctly.
A. Statuses & Health Check Actions
The Health Check shows the status of different AgileTest entities. Here’s what to look for:
a) Statuses
✅ Green Checkmarks: Everything works well! The entity has been initialized correctly.
 Orange Warnings: Something’s missing or not initialized properly. This could affect certain features.
Orange Warnings: Something’s missing or not initialized properly. This could affect certain features.
b) Action Buttons
Reverify: After making any changes or fixes, click Reverify to double-check the initialization status and ensure the updates were applied successfully.
Reinitialize: If an entity is missing or incorrectly initialized, click Reinitialize to restore the correct configuration and get everything back on track.
B. When To Use Health Check
You should use the Health Check feature if:
You encounter errors: If AgileTest is not working properly, it might be due to missing or incorrectly initialized entities.
Changes to the configuration: If any settings were accidentally deleted or modified, this could cause issues with AgileTest. Health Check can help confirm if anything is misconfigured.
AgileTest features aren’t working as expected: If certain features are missing or malfunctioning, run a Health Check to verify if all necessary configurations are present.
As a Jira Admin, you can run the Health Check to ensure everything is in place for AgileTest to function smoothly.
2. Enable AgileTest for Projects
On this page, you can enable or disable Agile Test plugin for specific projects. By default, AgileTest is enabled for all projects from your instance. To disable a specific project, simply search for specific ones and uncheck the checkbox.
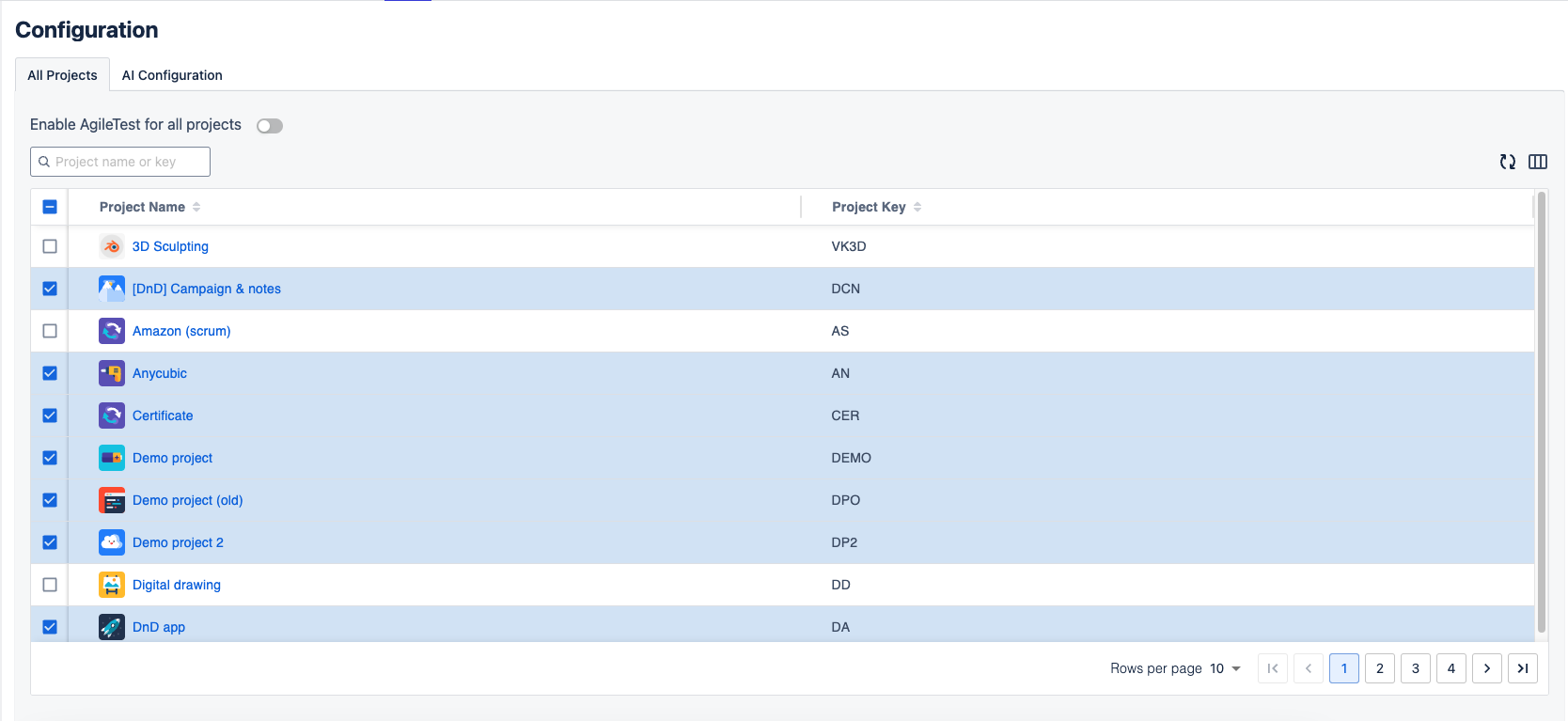
Once disabled, the project will no longer appear on the Agile Test main page, and users will not be able to access the app from the project screen.
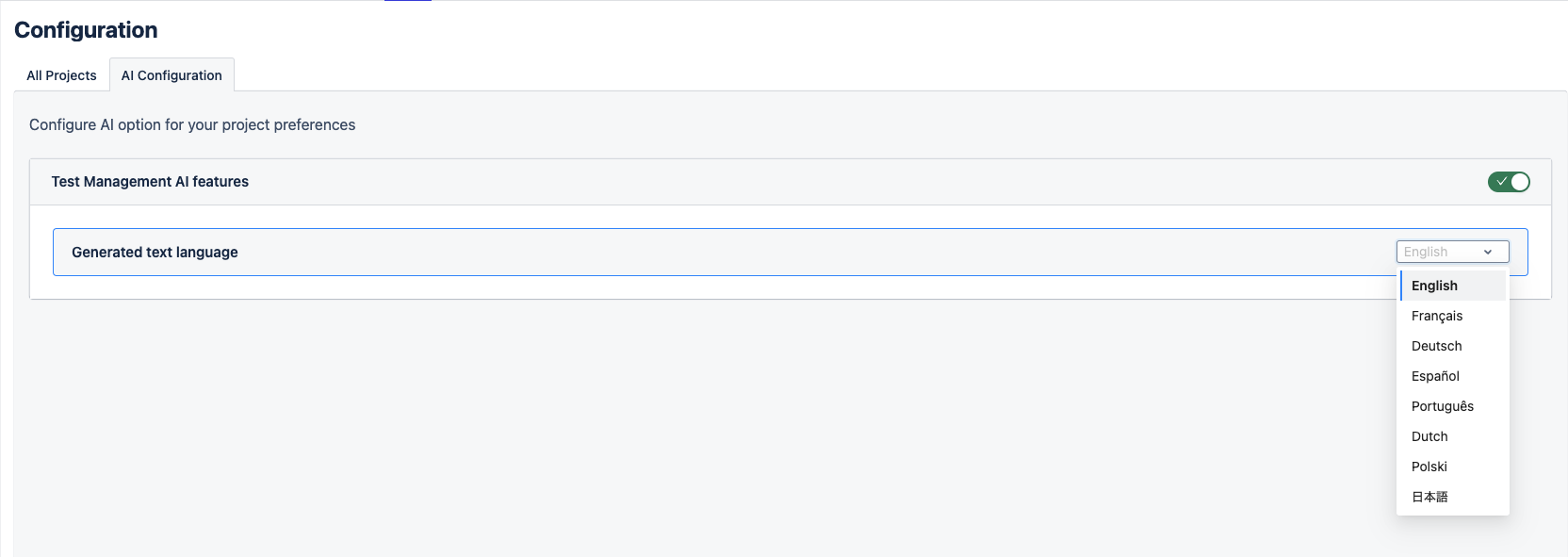
3. AI Configuration
The default language for AI generation is set to English. If you prefer a different language, simply select one from the dropdown list. Supported languages include English, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, Polish, Japanese, Korean, and Chinese.
For users who may not wish to use AI-generated content, this feature can be easily disabled at any time by switching off the toggle option.
4. Test Environments
A test environment refers to the setup or infrastructure needed to carry out software testing activities. It is a controlled, isolated environment specifically designed for testing, ensuring that the software performs as expected.
During testing, Test Executions will be frequently created, and each one should be linked to a Test Environment, indicating the platform on which your tests are being conducted.
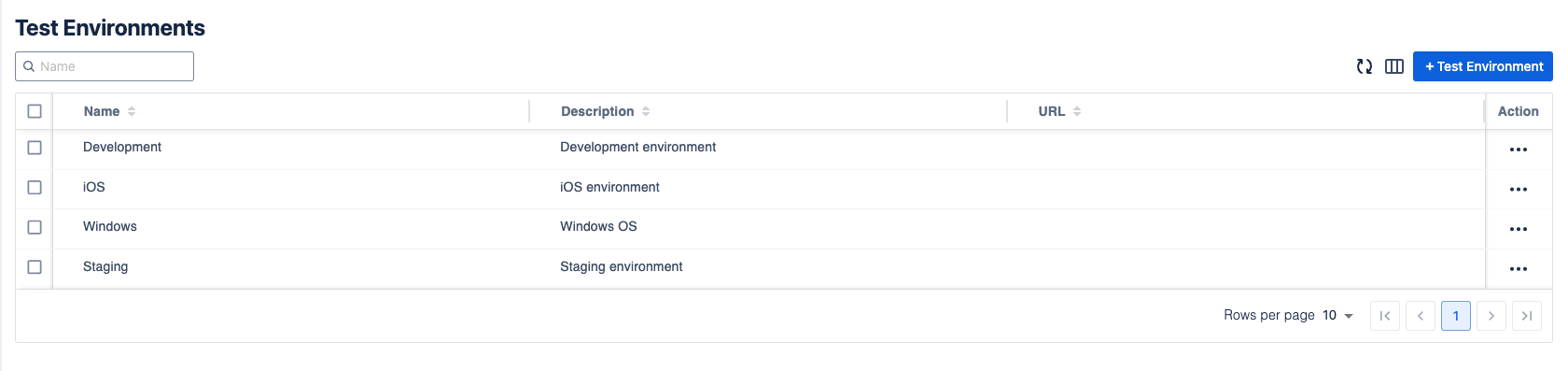
In order to add a new Test Environment, click on + New Test Environment button. Then fill in the information, and click on Create button.
5. Test Step Fields
Agile Test provides 3 default test step fields: Action, Data, and Expected Result. These step fields are flagged as DEFAULT and cannot be edited further.
However, these 3 step fields may not always be enough to fully define your test steps. You can create a custom step fields by choosing + New Test Step Field on the top right hand corner.
The custom step field is flagged as CUSTOM and can be enabled or disabled by selecting the option button in the Actions column.
The number of custom fields are limited to 7 only. If this limit is reached, user has 2 options
Update Existing Fields: Modify the details of your current custom fields to meet your needs.
Delete and Create New: Remove an existing custom field to make room for a new one.
Assignee is a step custom field, however it is not editable.
6. Test Step Statuses
In this setting, we allow users to manage available Test step statuses. The default statuses are To Do, Pass, and Fail. To add a new status, click + Test Step Status button.
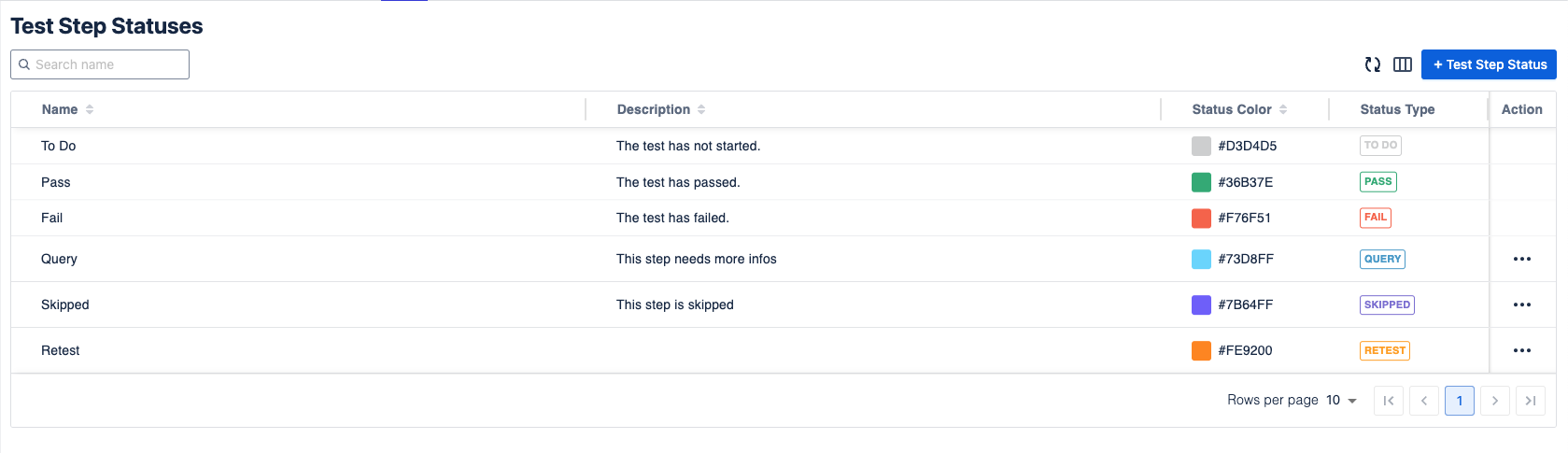
Remember to map the new status to one of built-in statuses. Doing that will ensure your test statistics are compiled and used to calculate the final Test run result.
7. Test Types
In Agile Test, there are 3 default test types: Manual, Generic, and Gherkin. Each is linked to one of the built-in types: Steps, Unstructured, and Gherkin, respectively. This setting allows you to configure and manage all test types in your instance.
Steps: Each test case consists of a list of test steps. During testing, users go through the test steps one by one and mark their status accordingly.
Learn more about Test execution here: Document!
Unstructured: Each test case contains a rich text field called 'Definition,' where you can input any details needed. This format is mainly used for automation tests, especially when test results are imported, either manually or automatically.
Gherkin: The test case is built using Gherkin scripts, which automatically support formatting and keyword prompts. With this type, you can utilize the common structure of 'Given, When, Then,' which defines the inputs, actions, and expected results for test steps.
Should you need any assistance or further AgileTest inquiries, contact here!
.png)