App project settings
Only Jira admins and Project admins can manage AgileTest project configuration
To access App project settings, go to ⚙️ Settings on AgileTest Sidebar → Settings → Project Settings. Below are the settings along with their explanations and configuration steps.
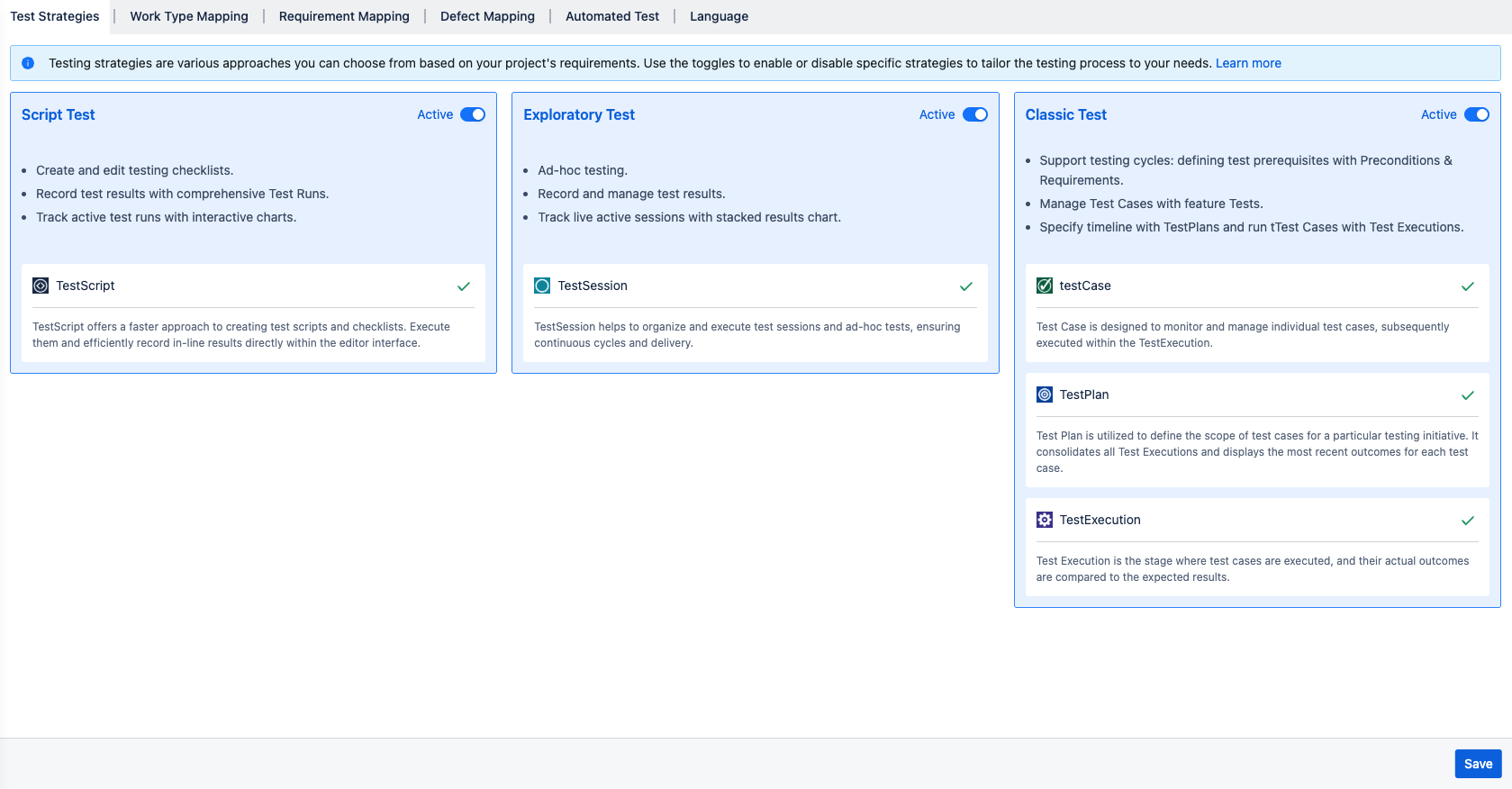
1. Test Strategies
On the first page, you can find settings for 3 Test strategies, they are:
Script Test: a checklist where you can write your own checklist or an outline and run tests and link defects on the fly.
(Learn more about Script Test → Document)Exploratory Test: constituted by Test Sessions on which you could run a timer and conduct exploratory or ad-hoc tests with a single click. After finishing, you can save elapsed time, and create and link the defects directly to your Test Session.
(Learn more about Exploratory Test → Document)Classic Test (Traditional Test Management): includes TestCase, TestPlan, and Test Execution. This type of strategy allows you to conduct your test in traditional manner by managing these test items in order, Test Plan → Test Execution → TestCase.
(Learn more about Classic Test → Document)
Users can enable or disable these strategies by switching the Active toggles on the top right hand of each board.
2. Work Type Mapping
The settings section allows users to map available work types to their respective AgileTest items.
Note: In Jira Cloud, you will find that 'work item' is the collective term for everything you track (e.g., tasks, bugs, stories). The specific categories of work, previously known as 'issue types,' are now generally referred to as 'work types.'
To learn more about creating new work types, please refer to this document from Jira
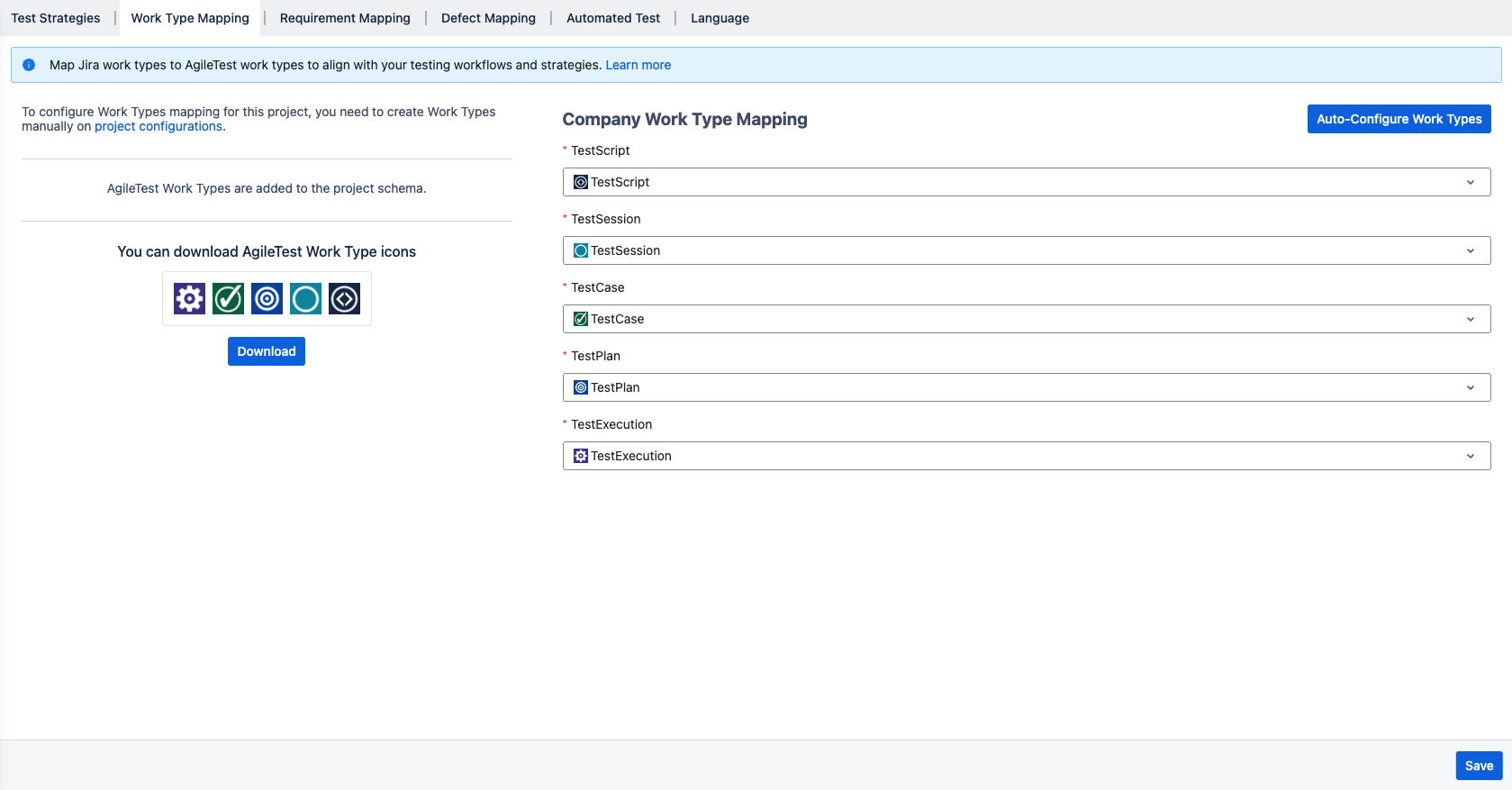
As you may know by now, we have 5 item types in AgileTest: Script Test, Test Session, Test Case, Test Plan, and Test Execution.
After you alter the work type mapping, the change will be reflected immediately in through out AgileTest → Please refer to project configuration.
3. Requirement Mapping
Changing work types mapping after a period of using the app could cause data lost. We recommend that you should finalize this configuration on the first access to the app in the new project.
To learn more about this, please refer to this document - Initiate your project with AgileTest.
This setting allows users to link and map their available Jira work types to AgileTest’s Requirements. Once mapped, these work types will appear as Requirements and can be managed directly within the app.
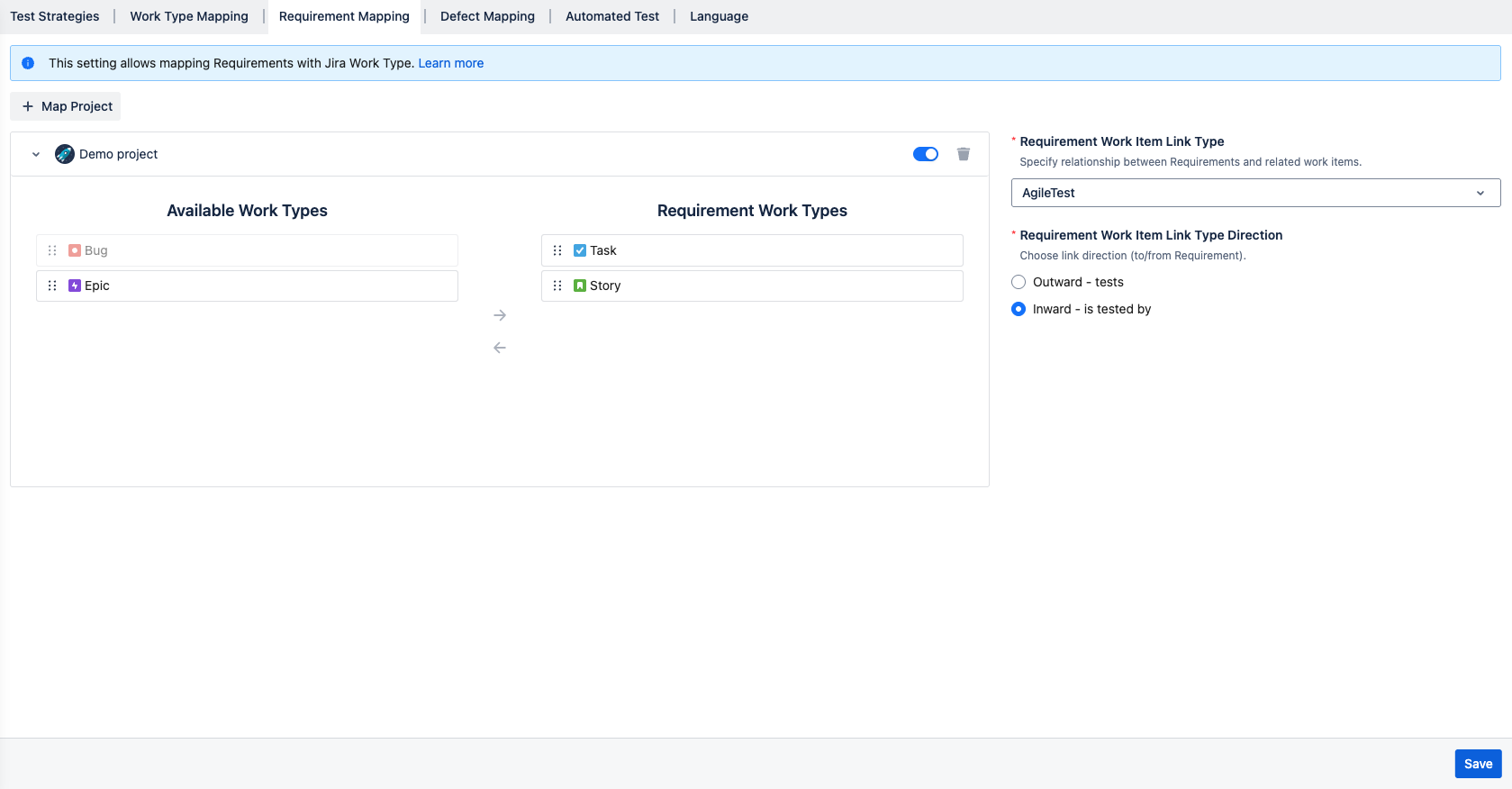
A. Default settings
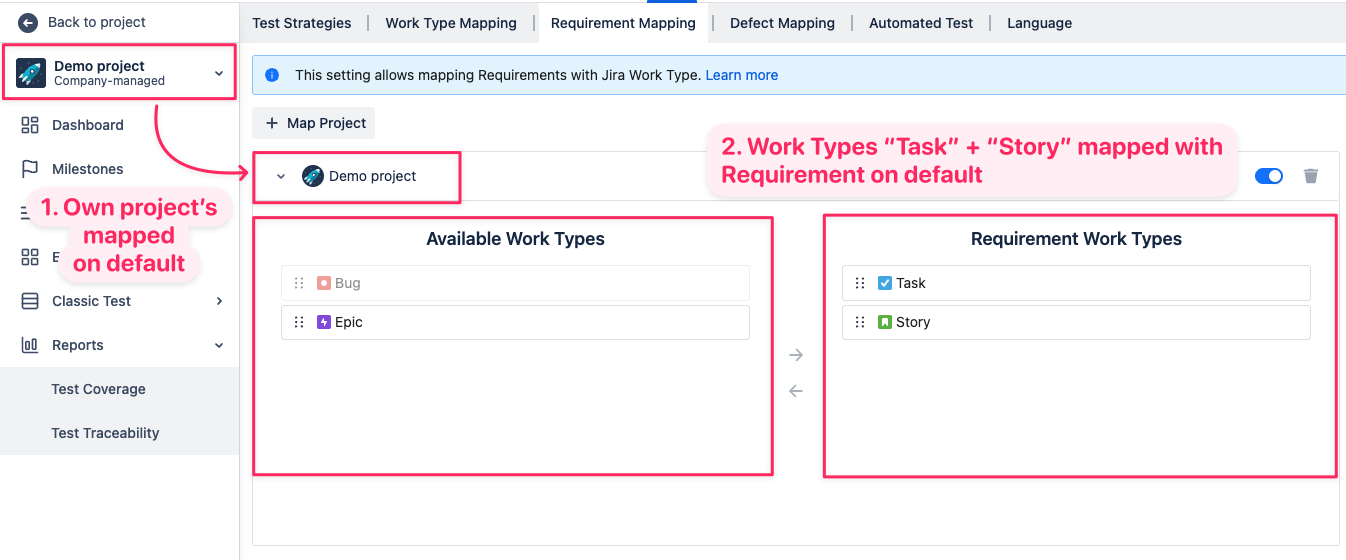
When first started, your project is automatically configured as default:
1. Map project: Your own project is mapped on default.
2. Work Types Mapping: Feature Requirements is mapped with 2 Jira Work Types: Task, and Story.
3. Requirement Work Item Link Type: Defines the relationship between AgileTest Requirements and Jira work items. By default, it is set to "AgileTest", which establishes the link between AgileTest's Requirements and the corresponding Jira work types.
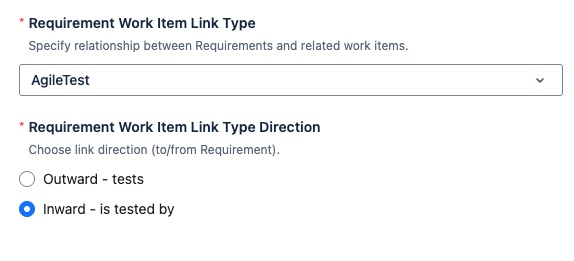
4. Requirement Work Item Link Type Direction: Is set to direction “Inward - is tested by“ by default.
Inward option - is tested by
On Requirement, it is read/understood as “Requirement is tested by Test case”.
On Test Case, it is read as “Test case tests Requirement”.
Outward option - tests
The direction is reversed as it is read/understood backward.
If you prefer to use a different link type, you can change it as needed. Otherwise, it’s recommended to keep the default value, “AgileTest”, for optimal integration.
To learn more about Link Types direction, read this document!
B. Custom settings
Besides default settings, you can customize your Requirement mapping:
1. Map Project: You can map up to 3 projects (including your own) from the same Jira instance. Once mapped, you’ll be able to manage work types as feature Requirements from those projects within your selected project. After mapping you can also disable/enable to disable project mapping.
This feature allows teams to centrally manage and track Requirements across multiple projects, enhancing cross-project visibility and collaboration.
2. Work Types Mapping: You can drag and drop individual or multiple Jira work items from the “Available Work Types” column to the “Requirement Work Types” column to map them to AgileTest’s Requirements.
Besides, you can also configure the Link types and its direction with this this document
4. Defect Mapping
Changing defect types mapping after a period of using the app could cause data lost. We recommend that you should finalize this configuration on the first access to the app in the new project.
To learn more about this, please refer to this document Initiate your project with AgileTest.
This setting allows users to link and map their available Jira work types to AgileTest’s Defect. Once mapped, these work types will appear as Requirements and can be managed directly within the app.
Note: AgileTest defects are also linked as Jira defects and can be fully managed within AgileTest.
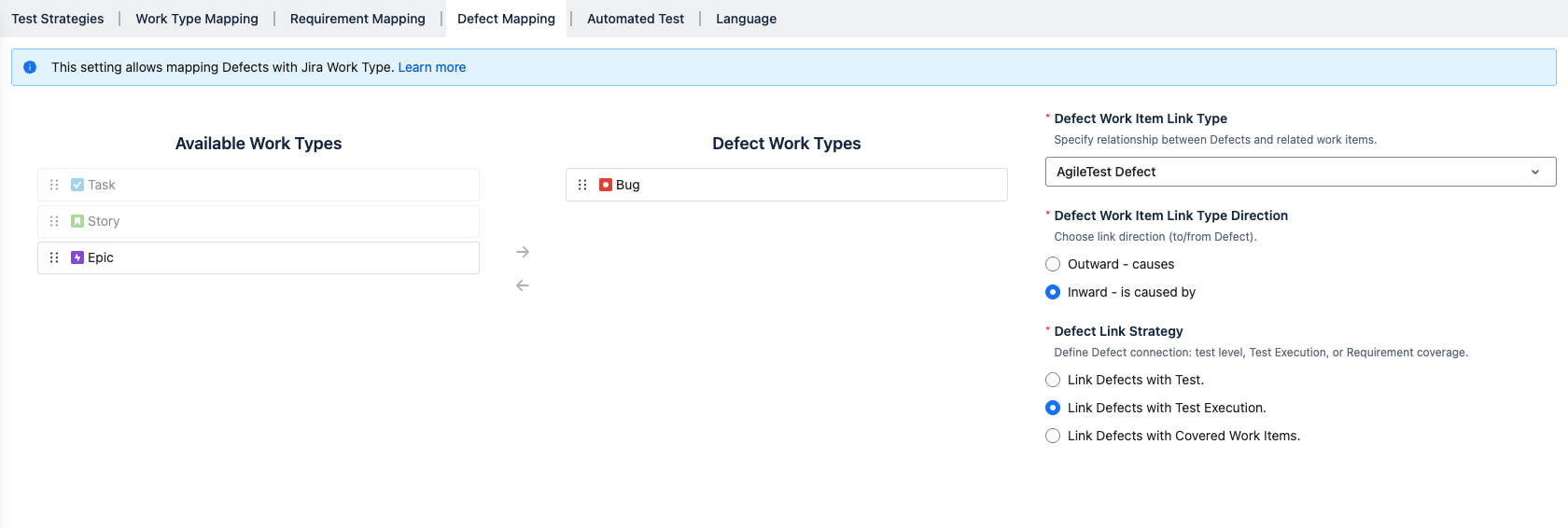
A. Work Type Mapping
Unlike the “Requirement Mapping” setting, defect linking is limited to a single project only.
AgileTest’s Defect on default is mapped with project’s Defect Work Type.
To map other work types, you can drag and drop individual or multiple Jira work items from the “Available Work Types” column to the “Defect Work Types” column to map them to AgileTest’s Defects.
B. Defect Link Type & Direction
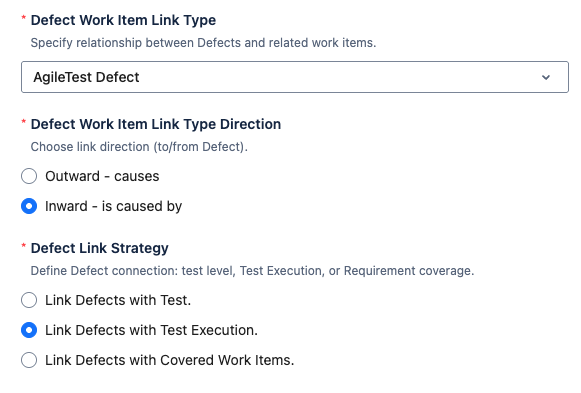
1. Defect Work Item Link Type
Defines the relationship between AgileTest Defects and Jira work items. By default, it is set to "AgileTest Defects", which establishes the link between AgileTest's Defects and the corresponding Jira work types.
If you prefer to use a different link type, you can change it as needed. Otherwise, it’s recommended to keep the default value, “AgileTest Defect”, for optimal integration.
To learn more about Link Types direction, read this document!
2. Defect Work Item Link Type Direction
The direction is set to “Inward - is caused by“ on default.
Inward option
On Defect, it is read/understood as “Defect is caused by Test Case”.
On Test Case, it is read as “Test Case causes Defect.
Outward option
The direction is reversed.
It is read/understood backward. This is only recommended when you want to customize your link, otherwise, you should select the Inward option as the default setting.
3. Defect Link Strategy
You can choose from three options to determine how Defects are linked during testing:
Link Defects with Test – Defects will be linked to the Test Case tickets.
Link Defects with Test Execution – Defects will be linked to the Test Execution tickets. (Default setting)
Link Defects with Covered Issues – Defects will be linked to the associated Requirement tickets.
By default, the system is set to Link Defects with Test Execution.
5. Automated Test configuration
A. Trigger configuration
1. Bitbucket
Firstly, click New Bitbucket Configuration button to reveal the configuration dialog.
User is required to fill in details as follows.
Please refer to this document to learn more about Bitbucket parameters - Run a pipeline with parameters.
Trigger Name: New trigger name.
Workspace: Your Bitbucket workspace.
Repository Slug: aka repo-slug, you can find it in your repository url
https://bitbucket.org/ <workspace-id>/<repo-slug>Body Data: we support Bitbucket parameters.
Example:
{
"target": {
"commit": {
"type": "commit",
"hash": "32fe523af85fe828ab97c70eb816ae1c9956d7b4"
},
"ref_type": "branch",
"type": "pipeline_ref_target",
"ref_name": "nunit"
}
}Repository Access Token: the access token of the current repository. To get one, please refer to this document from Jira Create a Repository Access Token.
Additional Parameters: additionally, we support extra params.
These fields are required only when a user creates a Test Execution without linking a Milestone, Test Plan, Test Environment, Revision, or Fix Version.
If the user has already provided these details, AgileTest will take them into account during the triggering process. The following cases may occur:
Field values already linked to the triggering Test Execution ticket: These values will be ignored.
Field values different from those linked to the triggering Test Execution ticket: The new values will be appended.
2. GitHub
Firstly, click New GitHub Configuration button to reveal the configuration dialog.
User is required to fill in details as follows:
Please refer to this document from GitHub for more details → Create a workflow dispatch event.
Trigger Name: New trigger name.
GitHub Owner: A string of your GitHub account name.
Repository Name: A string of the current repository.
Branch Name: A string of the branch on which we are going to trigger the workflow.
Inputs: This field allows users to add custom variables to send along with the triggering request. In most cases, it won't be necessary. However, in certain situations, it can be useful for integrating with additional setups in your GitHub workflow.
Access Token: A string of your Personal Access Token. To get one please refer to this document from GitHub Managing your personal Access Tokens.
Additional Parameters: additionally, we support extra params → Please go to Additional params.
3. GitLab
Firstly, click New Gitlab Configuration button to reveal the configuration dialog.
User is required to fill in details as follows:
Please refer to this document from GitLab for more details Trigger a pipeline with a token.
Trigger Name: New trigger name.
GitLab Project ID: A string of your GitLab project id. To get project id from GitLab main page go to Projects → Open your project → Copy project ID.
Branch Name: A string of the branch on which you want to trigger build.
Variables: This field allows user to add any custom variables to send along with triggering request. In most cases, you would not need it. However, in some special cases, it may provide a way to collaborate with further setups in your GitLab pipeline.
Pipeline Trigger Token: A string of your Pipeline trigger token. To create one please refer to this document from GitLab Create a trigger Token.
Additional Parameters: additionally, we support extra params → Please go to Additional params.
4. Jenkins
In AgileTest, we support 2 types of Jenkins jobs: Pipeline and MultiBranch.
Trigger Name: New trigger name.
Jenkins Username: A string of your Jenkins username.
Remote Jenkins URL: The URL to your Jenkins server, where you will run builds, e.g.
http://jenkins_url.Job Name: A string of the job which we are going to trigger.
Branch Name (only available for MultiBranch setting): Name of the branch on which we are going to trigger the pipeline.
Parameters: This field allows you to add custom variables when triggering a request. It's generally not required, but in some special cases, it can be useful for additional setups in your Jenkins jobs.
API Token: A string of your Jenkins API token.
To create a new API Token in your Jenkins instance, please follow these steps.
Log in to Jenkins.
Click your name (upper-right corner).
Click Configure (left-side menu).
Click Add API Token.
Additional Parameters: additionally, we support extra params → Please go to Additional params.
B. Execute build remotely
This step applies to any CI/CD configuration. Once the trigger setup is complete, open a Test Execution ticket.
On the right panel of the issue screen, under the Agile Test section, you will see the trigger you just created. Simply click Run to start your pipeline.
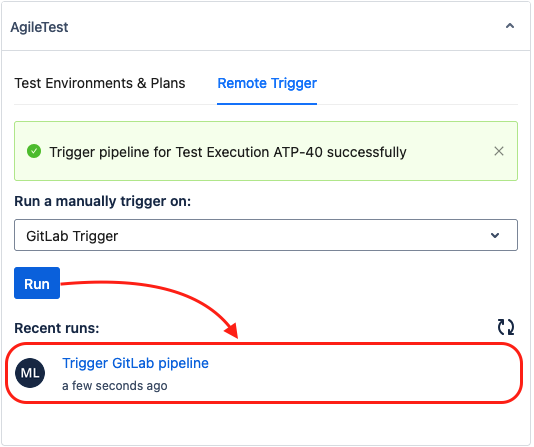
If everything is working correctly, clicking the Refresh button will display a confirmation message indicating that the pipeline has been triggered successfully.
6. Language
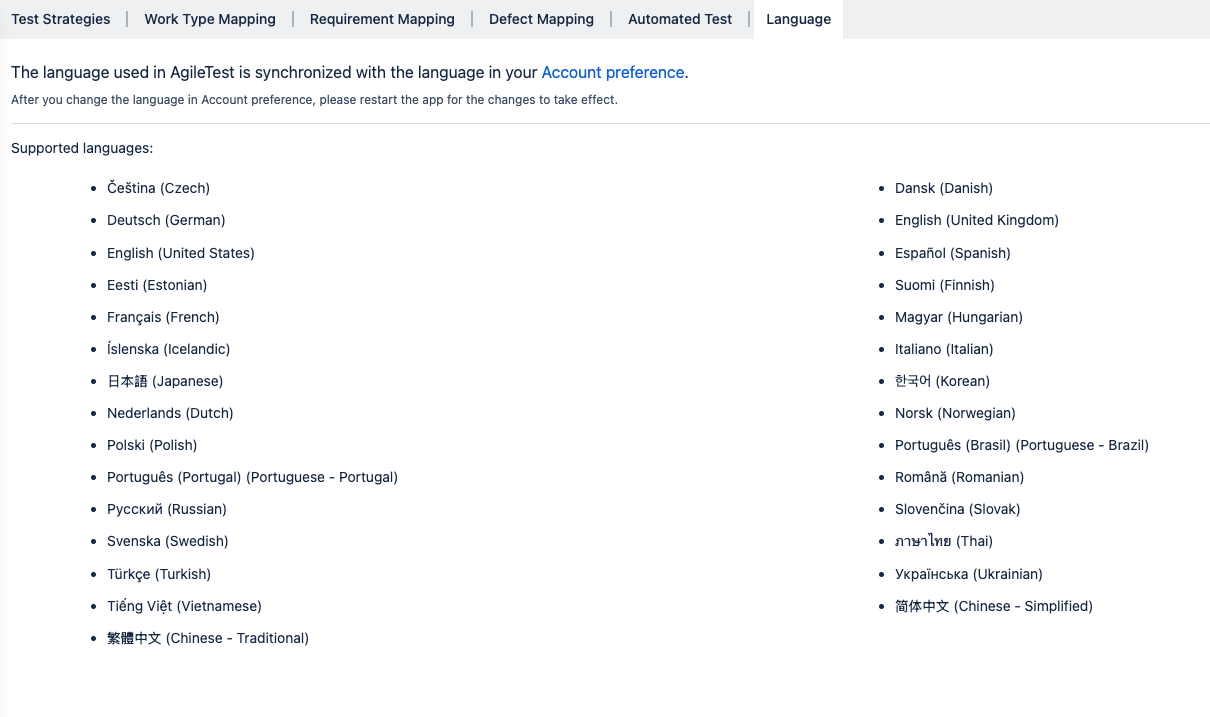
AgileTest supports multilingual usage by synchronizing its interface language with your Jira Account Preferences.
Note: After changing your preferred language in Jira, please refresh AgileTest for the changes to take effect.
After changing your Jira language preferences, AgileTest’s UI interface will be translated into the selected language.
To learn more about the Jira account preferences, read this Document.
Should you need any assistance or further AgileTest inquiries, contact here!
.png)